- 1 1. Understanding Fabric Weight: GSM and Tow Size Selection
- 2 2. Width Optimization: Minimizing Waste and Seams
- 3 3. Weave Pattern Mechanics: Plain vs. Twill in Body Contours
- 4 4. Material Innovation: Prepreg vs. Dry Fabric Rolls
- 5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 5.0.1 1. How many layers of carbon fiber are needed for a car hood?
- 5.0.2 2. Can I use an aerospace-grade carbon fiber roll for automotive parts?
- 5.0.3 3. What is the shelf life of a prepreg carbon fiber fabric roll?
- 5.0.4 4. Does fabric width affect the price per square meter?
- 5.0.5 5. What technologies does Jiangyin Dongli use for composite production?
- 6 Industry References
In high-performance automotive manufacturing, transitioning from traditional steel or aluminum to carbon fiber fabric roll materials is a strategic move to optimize the strength-to-weight ratio. However, the engineering success of a body panel depends heavily on selecting the correct textile specifications. Jiangyin Dongli New Materials Technology Co., Ltd., operating from a 32,000-square-meter precision-controlled industrial complex, specializes in high-performance fiber composite materials. With 100,000-grade purification zones and expertise in autoclave and RTM processes, we help engineers navigate the technical nuances of fabric selection for aerospace and automotive applications.
1. Understanding Fabric Weight: GSM and Tow Size Selection
The weight of a carbon fiber fabric roll is measured in grams per square meter (GSM), which directly correlates to the thickness and structural stiffness of the final panel. A common technical query for designers is: what is the best carbon fiber weight for car panels? For aesthetic exterior parts like hoods or mirror covers, a 200 GSM or 240 GSM fabric is standard. For structural reinforcement or larger floor pans, heavier weights like 400 GSM or 600 GSM are utilized to reduce the number of layers required during the layup process.
While 3K tow (3,000 filaments per bundle) is the industry standard for detailed curves and high-end visual finishes, 12K tow is significantly more cost-effective for large, flat structural reinforcements due to its thicker weave.
| Tow Size / Weight | Common GSM Range | Primary Automotive Use |
| 3K (Fine Weave) | 160g - 240g | Visible exterior panels, hoods, spoilers |
| 6K (Medium Weave) | 320g - 400g | Structural bracing, seat frames |
| 12K (Large Weave) | 400g - 1200g | Floor pans, chassis reinforcement, heavy industrial |
2. Width Optimization: Minimizing Waste and Seams
The width of the carbon fiber fabric roll is an often overlooked variable that impacts both production cost and structural integrity. One must ask: how to calculate carbon fiber fabric width for automotive hoods? Standard widths usually range from 1000mm to 1500mm. Choosing a width that exceeds the widest point of the panel allows for "one-piece" draping, which is essential for maintaining the continuous fiber path required for crash-energy management. Jiangyin Dongli provides custom width options to ensure that automotive manufacturers can minimize off-cut waste during precision CNC cutting.
Compared to narrow rolls which require overlapping seams—introducing potential weak points and visual inconsistencies—wide-format rolls allow for a seamless aesthetic that is crucial for high-end automotive "naked carbon" finishes.
| Width Specification | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Narrow (300mm - 500mm) | Easier handling for small trim parts | Frequent seams on large panels |
| Standard (1000mm - 1270mm) | Industry standard for most doors and fenders | Moderate waste on irregular shapes |
| Wide (1500mm+) | Seamless draping for roofs and hoods | Requires larger clean-room cutting tables |
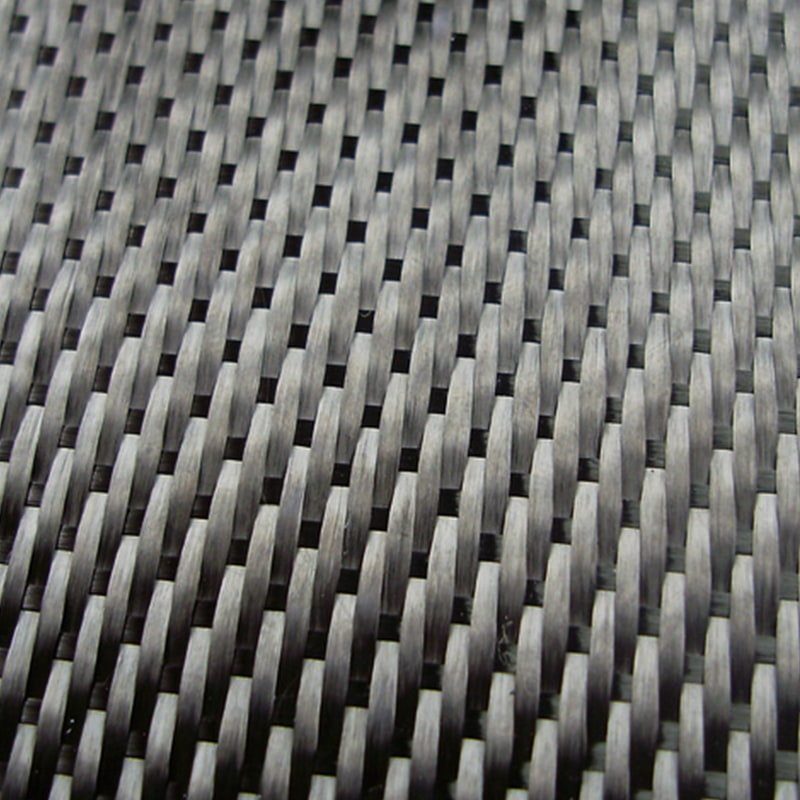
3. Weave Pattern Mechanics: Plain vs. Twill in Body Contours
The geometry of automotive panels—ranging from flat roofs to complex, aerodynamic bumpers—dictates the necessary weave pattern. A frequent technical question is: is twill or plain weave better for carbon fiber car parts? Twill weave (2x2 or 4x4) is prized in the automotive sector for its superior drapability, allowing the carbon fiber fabric roll to conform to tight radii without distorting the fiber orientation. Jiangyin Dongli New Materials Technology Co., Ltd. utilizes advanced weaving and prepreg processes to ensure that these patterns remain stable during the PCM and WCM (Wet Compression Molding) phases.
- Drapability: Twill weave flows over curves more easily than tight plain weaves.
- Structural Integrity: Why use unidirectional carbon fiber for automotive frames? For chassis components, unidirectional (UD) fabric is often interleaved with woven fabric to provide targeted strength in specific load paths.
- Processing: Our RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) technology is optimized for high-permeability weaves that ensure complete resin wet-out.
4. Material Innovation: Prepreg vs. Dry Fabric Rolls
For high-tier automotive manufacturing, the benefits of prepreg carbon fiber vs dry fabric are significant. Prepreg rolls are pre-impregnated with a precise ratio of epoxy resin and stored in climate-regulated workshops. This eliminates the "human factor" in resin application, resulting in panels with a higher fiber volume fraction and lower weight. Jiangyin Dongli integrates material innovation with engineering expertise to provide one-stop factory solutions for those moving toward autoclave-cured prepreg components.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How many layers of carbon fiber are needed for a car hood?
Typically, 2 to 3 layers of 200-240 GSM carbon fiber fabric roll are used. The outer layer is usually a 3K twill for aesthetics, while inner layers may be 6K or UD for structural stiffness.
2. Can I use an aerospace-grade carbon fiber roll for automotive parts?
Yes. High-performance fiber composite materials designed for aerospace often feature higher tensile strength and better resin systems, making them excellent for ultra-lightweight racing components.
3. What is the shelf life of a prepreg carbon fiber fabric roll?
In a climate-regulated workshop at -18°C, prepreg can last 6 to 12 months. At room temperature, the "out-life" is typically only 5 to 30 days depending on the resin system.
4. Does fabric width affect the price per square meter?
Generally, no. However, choosing the correct carbon fiber fabric roll width significantly reduces waste, which lowers the "total part cost" by as much as 15-20%.
5. What technologies does Jiangyin Dongli use for composite production?
We utilize a full suite of advanced technologies, including autoclave, RTM, RMCP, PCM, WCM, and specialized spraying technologies to meet diverse industrial requirements.
Industry References
- ISO 15024: Fiber-reinforced plastics — Determination of mode I interlaminar fracture toughness.
- SAE International: "Advanced Composite Materials for Automotive Body Structures."
- ASTM D3039: Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials.
- Technical Production Manual: Jiangyin Dongli New Materials Technology Co., Ltd. (2026 Edition).
 English
English  中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt