Manufacturing process of carbon fiber woven cloth: mechanical properties comparison of plain, twill and satin
1. Basic concept of carbon fiber woven cloth
Carbon fiber woven cloth (Carbon Fiber Woven Cloth) is a two-dimensional or three-dimensional structural material made of carbon fiber tow (Tow) through a specific weaving method. It has the characteristics of high strength, high modulus, and lightweight. It is widely used in aerospace, automobile, wind power, sports equipment and other fields.
2. Three main weaving methods and their structural characteristics
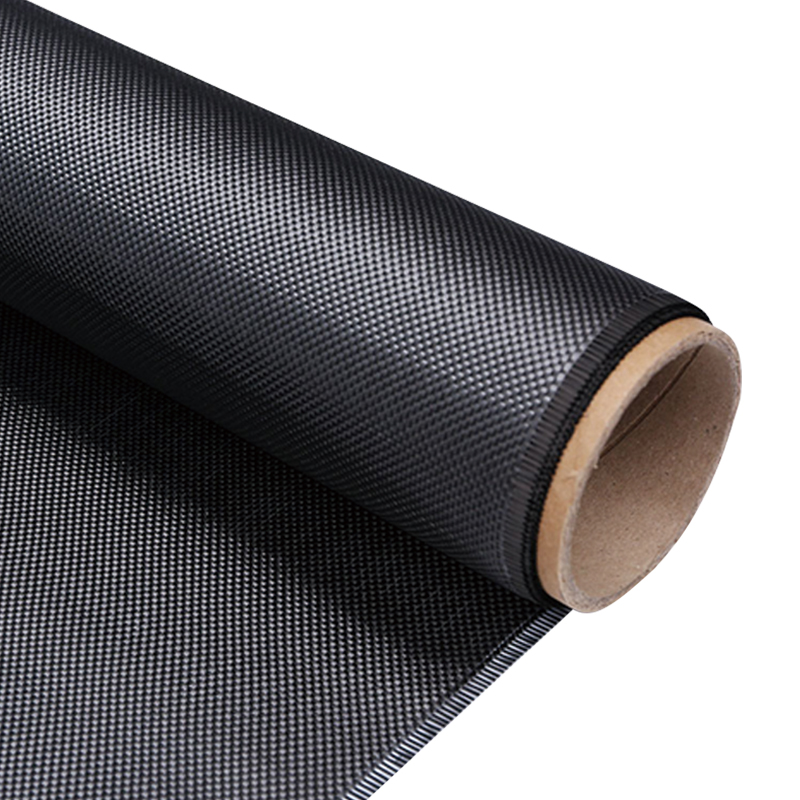
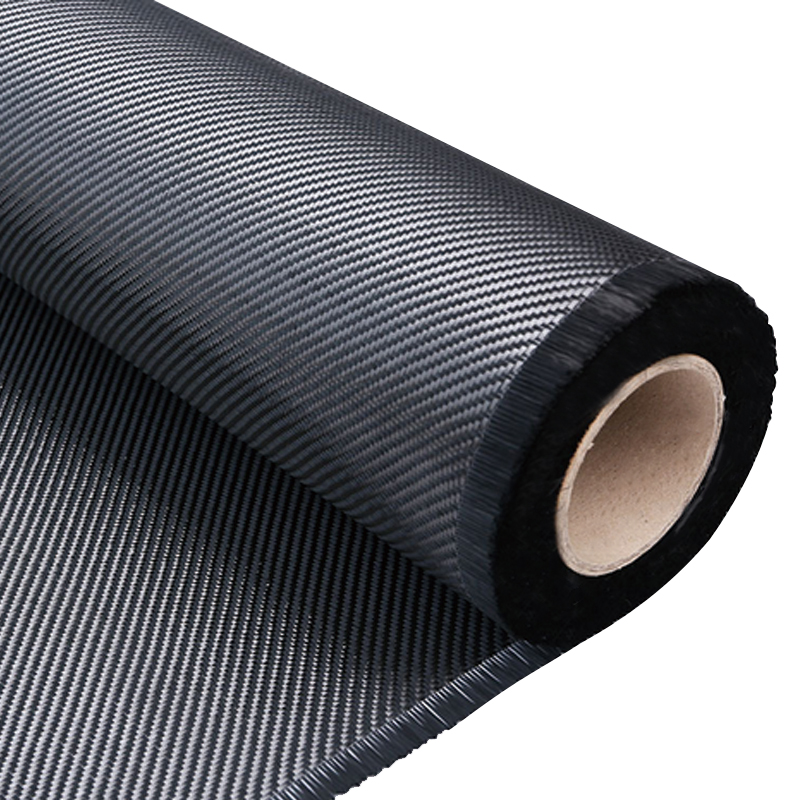
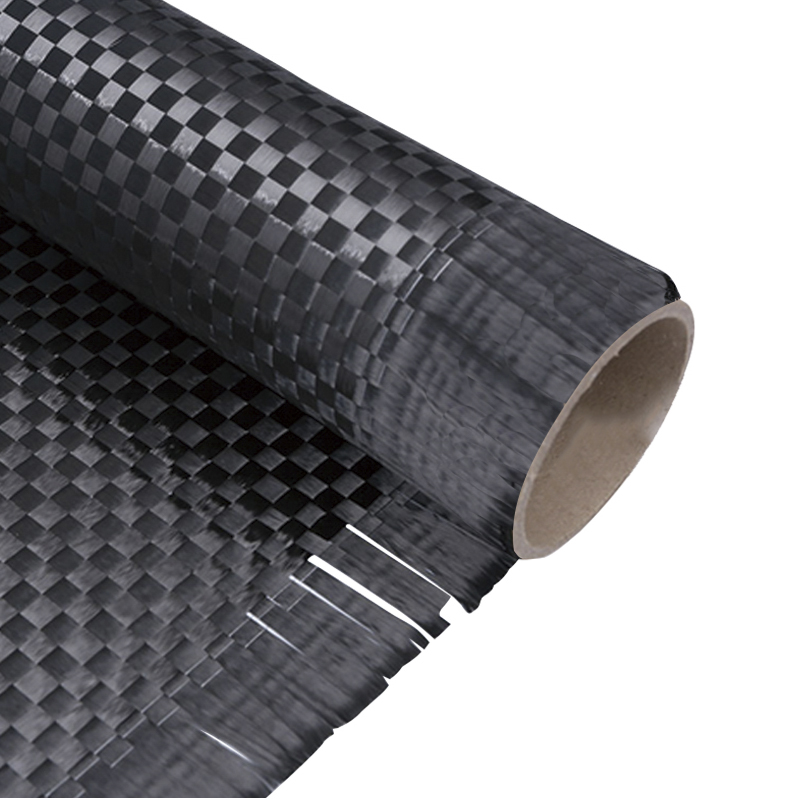
The main weaving methods of carbon fiber woven cloth include plain weave, twill weave, and satin weave. They have significant differences in fiber arrangement, interweaving methods and mechanical properties.
| Weave Type |
Structural Characteristics |
Interlacing Frequency |
Surface Smoothness |
Formability |
| Plain Weave |
Warp and weft yarns alternate in a 1:1 over-under pattern |
High (many interlacing points) |
Low (visible texture) |
Moderate (prone to wrinkling) |
| Twill Weave |
Warp and weft yarns interlace in a 2:2 or 4:4 diagonal pattern |
Medium |
Moderate (diagonal pattern) |
Good (flexible) |
| Satin Weave |
Warp and weft yarns interlace in a 4:1 or 8:1 long-float pattern |
Low (few interlacing points) |
High (smooth surface) |
Best (conforms well to complex curves) |
3. Comparison of mechanical properties
Different weaving methods directly affect the mechanical properties of carbon fiber composite materials. Key indicators include tensile strength, bending stiffness, interlaminar shear strength (ILSS) and impact resistance.
| Property |
Plain Weave |
Twill Weave |
Satin Weave |
| Tensile Strength |
High (tight interlacing provides stability) |
Medium (balanced strength and flexibility) |
Low (fiber slippage risk in long floats) |
| Bending Stiffness |
Highest (compact structure) |
Medium |
Low (straighter fiber paths) |
| Interlaminar Shear Strength (ILSS) |
High (interlacing enhances bonding) |
Medium |
Low (potential delamination) |
| Impact Resistance |
Good (interlaced fibers distribute stress) |
Good |
Moderate (long floats may delaminate) |
| Drapeability |
Poor (tends to wrinkle) |
Good |
Best (conforms to complex shapes) |
4. Comparison of applicable scenarios
Plain weave: suitable for structural parts that require high rigidity and stability, such as drone fuselages and racing chassis.
Twill: Balances strength and formability, commonly used in automotive exterior parts (such as carbon fiber hoods) and sports equipment (bicycle racks).
Satin: Suitable for complex shapes with high curvature, such as aircraft wings, high-end helmets, and ship parts.
5. Future development trends
Hybrid weaving technology: Combine different weaving methods to optimize local mechanical properties (such as plain weave + satin composite structure).
3D weaving technology: Improve Z-direction strength and reduce the risk of interlayer delamination.
Smart weaving: Combine sensor fibers to achieve structural health monitoring.
 English
English
 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt